Who’s leading the race to develop electric vehicles in Southeast Asia? The answer is complicated.
Who’s leading the race to develop electric vehicles in Southeast Asia? The answer is complicated.
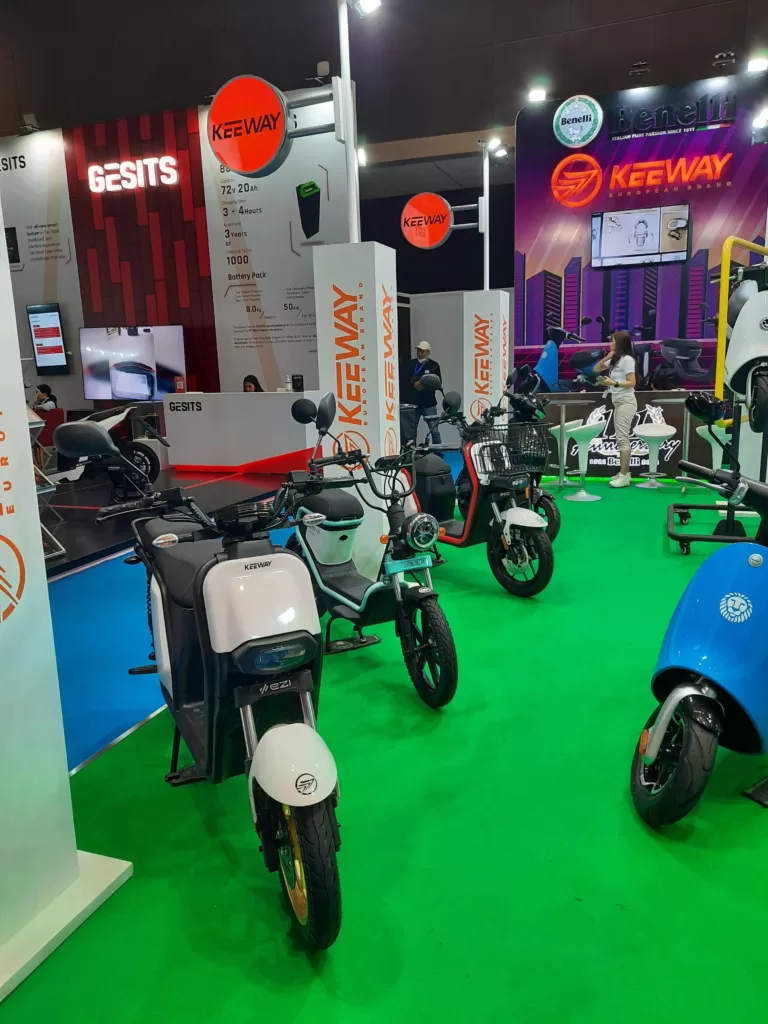
Southeast Asia is racing to increase the demand and production of electric vehicles.
With road vehicles responsible for 89 percent of transport-related pollution in the region, EVs are not only seen as part of the solution to reducing carbon emissions but also a way to drive new investments leading to more jobs, stronger economic development and technological advances.
Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam are leading the charge.
But it’s a long road. EV market penetration is still low. EV sales were just 2.1 percent of total vehicle sales in Southeast Asia in 2022, compared to 2.3 percent in India and 29 percent in China.
The slow development of charging infrastructure and the relatively higher cost of EVs, which are usually imported, are to blame.
While each nation is using tools such as subsidies and tax exemptions to reduce the cost of EVs for consumers, building electric vehicles and their components in-country is seen as the key to accelerating the industry.
Indonesia, for instance, is subsidising the cost of converting motorbikes to electric along with installing more charging stations and encouraging local vehicle assembly in the bid to lower prices.
The EV supply chain comprises mining and processing minerals, battery production, battery swapping, semiconductors, EV production/assembly, battery recycling, along with research and development.
The battery is the heart of EV production, so each country is eager to jump-start their EV battery industry.
Indonesia is leading the race due to its large nickel reserves which are banned for export to assist the shift towards activities such as the manufacture of lithium-ion batteries (see graphic).
But the others are catching up with the discovery of critical minerals in Malaysia as well as the reported mining of nickel in Vietnam by Australian company, Blackstone Minerals, for production in 2025.
New EV batteries are being developed that will reduce the use of nickel to a combination of minerals that are more readily available and cost-effective.
Battery swapping is one way to overcome the limitations of charging infrastructure and to reduce the time needed for charging batteries, especially for bikes.
This has gained traction in some big cities through various companies: Swap Energy in Indonesia, Blueshark Ecosystem in Malaysia, Swap and Go in Thailand and Selex Motors in Vietnam.
The production of semiconductor chips is concentrated mainly in Malaysia and Thailand with Germany’s Infineon Technologies building a plant in Malaysia for the production of EV batteries.
E-bikes have already taken off with assembly operations found in all four countries. Hyundai has a factory about 40km from Jakarta while Volvo is assembling plug-in hybrid vehicles in Malaysia.
Mercedes Benz is assembling plug-in hybrids in Thailand, whereas local manufacturer Vinfast is manufacturing battery electric vehicles in Vietnam. Vietnam is the first country in Southeast Asia with a domestic producer.
Recycling EV batteries is important for sustainability since the minerals used for production are scarce. Recycling will also help to reduce the environmental impact of mining these scarce resources.
However, recycling is still in its infancy in Southeast Asia since many of the EVs in use have not reached the stage of having to deal with battery disposal. Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam are planning recycling facilities with different partners.
Research and development for EVs is also just budding since the technology for EV assembly is sourced from foreign investors and manufacturers. Vinfast’s R&D centre in Melbourne closed down in 2021 due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
Vingroup, the parent company of Vinfast, is investing in battery research and development. China Automotive Technology and Research Centre is establishing a regional office in Thailand.
Proton in Malaysia is working on the development of a homegrown EV for Malaysia, that would include esearch and development activities.
The shift to EVs has to be accompanied with a shift towards a greener grid. Fossil fuels are still the major sources of electricity for Thailand, Indonesia and Malaysia, accounting for at least 80 percent of electricity production.
Vietnam is the most advanced in using renewables for its electricity production. While there are plans in each country to green the grid, it remains to be seen whether the stated targets can be achieved.
Southeast Asian nations are keen to shift away from internal combustion engines to EVs.
With policies in place to encourage this transition, the EV sector is on the cusp of momentous change, including the shift towards domestic production and assembly.
At the same time, there are tremendous technological changes, especially with batteries.
This provides opportunities for other countries to hitch a ride on the EV juggernaut.
However, it is important for each nation to increase the use of renewables so each can benefit from the use of EVs to facilitate the shift towards lower carbon transmissions.
Tham Siew Yean is Visiting Senior Fellow at the ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute and Emeritus Professor at Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia.
This article is being republished as part of a series on electric vehicles. It was originally published on October 30 as part of a Special Report on Energy Transition.
Originally published under Creative Commons by 360info™.
Editors Note: Tham Siew Yean, ISEAS-Yusof Ishak Institute